A Comprehensive Guide to Flap Techniques for Implant Placement
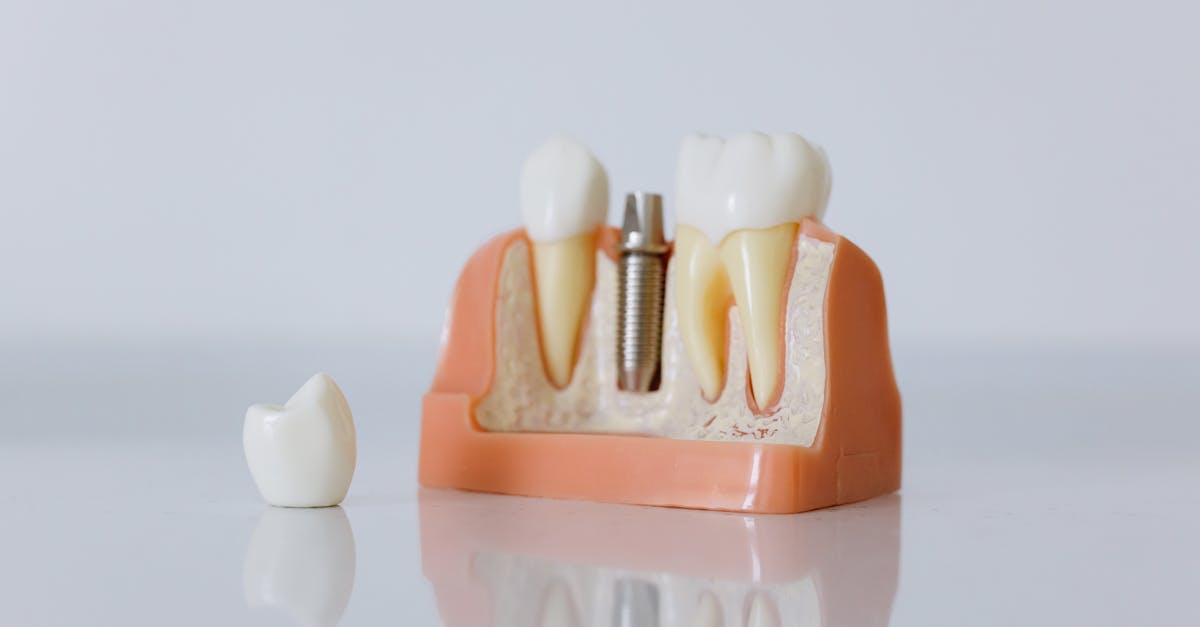
Table Of Contents
Surgical Steps for Partial-Thickness Flap
The procedure begins with the careful administration of local anaesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort. The area is then meticulously prepared, with surgical drapes placed to maintain a sterile environment. Using a scalpel, the clinician makes precise incisions into the mucosa and underlying tissues, creating a partial-thickness flap. It is crucial to ensure that the periosteum remains intact during this initial incision to preserve blood supply to the overlying soft tissue.
Once the flap is elevated, attention shifts to adequately exposing the implant site. The clinician gently reflects the flap away from the bone, taking care not to damage the surrounding structures. This step is essential to prepare the site for implant placement. Continuous assessment of flap vitality occurs throughout the procedure, with particular attention paid to maintaining the integrity of the blood supply, which is vital for postoperative healing. Proper tension on the flap is also monitored to ensure that it can adequately cover the implant once placed.
Technique Breakdown
The technique involves several key steps to ensure an effective flap formation, beginning with anaesthesia administration. Following this, a precise incision is made to create the flap, mindful of preserving underlying tissues for optimal healing. The flap is typically raised in a manner that allows adequate access to the underlying bone without excessive trauma. This careful approach aids in minimising complications post-surgery and facilitates a smoother recovery.
During the procedure, it's essential to maintain a clear surgical field to enhance visibility and reduce the risk of inadvertent damage to adjacent structures. Once the flap is elevated, careful inspection of the area is vital to assess the quality of the bone and surrounding tissues. Adequate irrigation should be performed to remove debris and maintain a clean operative site. Finally, the flap is repositioned with attention to tension-free closure, preserving the blood supply, which is crucial for successful integration of the implant.
Postoperative Care and Maintenance
Effective postoperative care is crucial for ensuring the successful healing of flap techniques used in implant placement. First, it is important to maintain an appropriate level of hygiene around the surgical site. Patients should be instructed to gently rinse with a prescribed antiseptic mouthwash to reduce the risk of infection. Regular follow-up appointments should be scheduled to monitor the healing progress, making it easier to address any potential complications early on.
Post-surgical discomfort can often be managed with prescribed pain relief medication. A soft diet is recommended for the initial recovery period to minimise stress on the surgical site. Patients should also be advised to refrain from strenuous physical activities that could disrupt the healing process. Proper education about care practices, such as avoiding smoking and controlling any pre-existing conditions, plays a significant role in enhancing recovery outcomes.
Ensuring Proper Healing
After the surgical procedure, meticulous attention to wound care plays a vital role in the healing process. The surgical area should remain clean and dry, minimising the risk of infection. Regular monitoring for signs of swelling or discharge can help detect any issues early. Patients are advised to follow specific instructions regarding oral hygiene, as maintaining a clean environment around the implant site is crucial for successful healing.
Adequate nutrition can significantly impact recovery. A diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports tissue regeneration and overall well-being. It is also essential for patients to remain hydrated and avoid activities that can stress the surgical site. Regular follow-ups with the dental professional ensure any complications are identified promptly and addressed effectively.
Complications and How to Manage Them
Flap techniques, while generally safe and effective, can sometimes lead to complications that may hinder the healing process or the success of the implant placement. One common issue observed is flap necrosis, which occurs when the blood supply to the flap is compromised. Factors such as inadequate flap design, excessive tension, or underlying systemic conditions can exacerbate this problem. Careful monitoring is essential; if necrosis is detected early, intervention strategies might include surgical revision or more conservative management to salvage the tissue.
Another issue that practitioners may encounter is infection at the flap site. Signs such as increased redness, swelling, or purulent discharge may indicate an infectious process that requires prompt attention. Maintaining a sterile technique during the procedure and ensuring patients adhere to postoperative care instructions can significantly reduce the risk of infection. If an infection does occur, management typically involves appropriate antibiotic therapy and, in some cases, drainage of any abscess that forms. Close follow-up is vital to ensure that the healing trajectory stays on course.
Common Issues with Flap Techniques
Flap techniques, while beneficial for implant placement, can present various challenges that clinicians must navigate. Complications such as flap necrosis can arise, often due to insufficient blood supply. Factors contributing to this issue include excessively tight sutures or improper flap design. Additionally, infection may occur if aseptic techniques are not thoroughly followed, leading to delayed healing and compromised implant success.
Another significant issue involves the potential for flap dehiscence, where the edges of the flap fail to properly close. This can be attributed to factors such as excessive tension on the closure or inadequate approximation of the tissue. Patient-related factors, including smoking and systemic health conditions, can further exacerbate these issues. Addressing these common complications demands a thorough understanding of surgical techniques and vigilant postoperative care to optimise outcomes.
FAQS
What is a flap technique in implant placement?
A flap technique in implant placement involves creating a surgical flap of tissue to provide access to the underlying bone and facilitate the placement of dental implants.
What are the key steps involved in the partial-thickness flap technique?
The key steps for a partial-thickness flap technique include making an incision in the gum tissue, carefully reflecting the flap to expose the bone, placing the implant, and then repositioning and suturing the flap to ensure proper healing.
How can I ensure proper healing after a flap surgery?
To ensure proper healing after flap surgery, it is crucial to follow the postoperative care instructions provided by your dentist, which may include maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding certain foods, and attending follow-up appointments.
What are some common complications associated with flap techniques?
Common complications associated with flap techniques include infection, flap necrosis, delayed healing, and implant failure. It’s important to recognise these issues early and consult your dentist for appropriate management.
How can complications from flap techniques be managed effectively?
Complications can be managed effectively through prompt intervention, including antibiotic therapy for infections, careful monitoring of the healing process, and in some cases, surgical revision if necessary. Always communicate any concerns with your dental professional.
Related Links
Choosing Between Single-Stage and Two-Stage Dental Implant SurgeriesUnderstanding the Role of Bone Grafting in Dental Implant Surgery
Assessing Injection Techniques for Anesthesia in Implant Surgery
Exploring the Use of PRP in Enhancing Implant Success Rates
Evaluating the Importance of Soft Tissue Management in Implant Surgery
Techniques for Managing Sinus Lift Procedures During Implant Placement
The Benefits of Minimally Invasive Implant Surgery Techniques
Advancements in Computer-Guided Implant Surgery
The Use of Guided Bone Regeneration in Dental Implant Procedures