Diagnostic Imaging Techniques for Effective Implant Planning
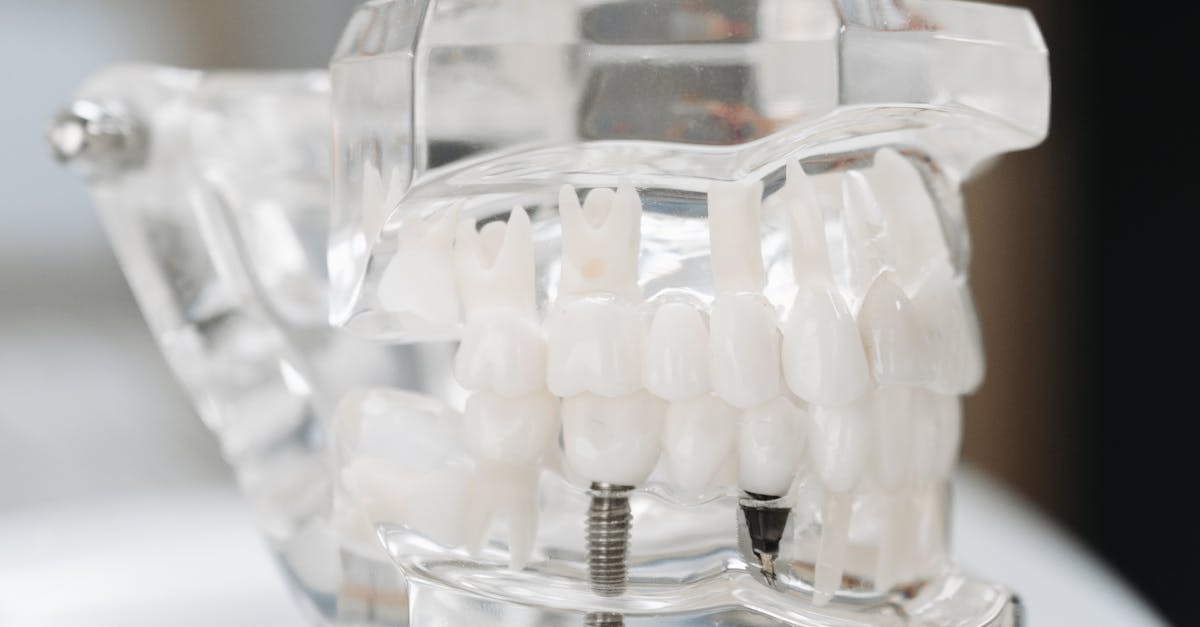
Table Of Contents
3D Imaging Techniques
Three-dimensional imaging techniques have transformed the landscape of implant planning. Techniques such as Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) provide high-resolution images that detail both hard and soft tissue structures. This level of detail allows clinicians to accurately assess the available bone for implant placement, ensuring a precise fit that aligns with the patient's anatomical requirements. The 3D models generated can be manipulated and viewed from various angles, offering a comprehensive perspective that traditional 2D images cannot provide.
Utilising 3D imaging also enhances communication between the surgical team and the patient. Visual representations of the planned implant site help demystify the procedure for patients, fostering a clearer understanding of the treatment plan. Moreover, advanced software can simulate potential outcomes, assisting both clinicians and patients in making informed decisions about the best approach to implant therapy. This integration of imaging technology not only improves surgical accuracy but also contributes to enhanced patient satisfaction.
Enhancing Accuracy with 3D Models
The use of 3D models in implant planning significantly enhances surgical precision. These models provide a more comprehensive view of the complex anatomy compared to traditional 2D imaging. Surgeons can visualise the spatial relationships between dental structures, enabling them to develop tailored implant placement strategies. This detailed representation allows for meticulous planning and reduces the risk of complications during the actual procedure.
Customised 3D models facilitate better communication among the dental team. They serve as visual aids during consultations, helping patients understand the proposed treatment plan. Moreover, these models can be utilised for educational purposes, allowing newer practitioners to gain insight into the intricacies of implantology. By bridging the gap between technology and clinical practice, 3D models contribute to improved outcomes for both patients and practitioners alike.
The Importance of Digital Imaging
Digital imaging has transformed the landscape of dental implantology, facilitating precise diagnosis and treatment planning. Techniques such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and digital radiography allow for enhanced visualisation of the anatomical structures, providing clear insights into the patient's oral environment. These tools not only improve the accuracy of assessments but also enable practitioners to identify potential complications before embarking on the surgical process.
Moreover, the integration of digital imaging technology streamlines workflow and enhances communication between dental professionals and patients. Detailed images can be shared easily, making collaborative decisions more straightforward. This transparency often leads to increased patient comfort and confidence in the proposed treatment plans, ultimately aiming for improved clinical outcomes. The adoption of digital methods also fosters a more efficient approach to record-keeping and follow-up assessments.
Integrating Digital Technology in Implantology
The integration of digital technology into implantology has revolutionised planning and execution processes. Advanced software tools enable clinicians to create detailed digital models from imaging data, allowing for meticulous pre-surgical analysis. These models facilitate the assessment of patient-specific anatomical features and variations, essential for developing tailored treatment plans.
Moreover, digital workflows streamline communication among dental professionals. Implant placement can be simulated in a virtual environment, offering insights into optimal angles and positions prior to surgery. This approach enhances collaboration, as technicians and surgeons can review and adjust plans collectively, promoting a comprehensive understanding of the patient's needs.
Evaluating Anatomy and Bone Density
Anatomical evaluation is crucial in the planning of dental implants. Various imaging techniques, such as Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), provide detailed visualisation of the underlying structures, allowing practitioners to assess bone quality and quantity. This comprehensive view aids in identifying vital anatomical landmarks, such as nerves and sinuses, ensuring that implants can be placed safely and effectively. The precision of 3D imaging also enhances the understanding of individual patient anatomy, which can vary significantly, making tailored approaches more feasible.
Bone density analysis is essential for predicting the success of implant integration and longevity. By evaluating bone density, practitioners can ascertain whether a site is suitable for immediate implantation or if additional augmentation procedures are necessary. Techniques like dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) can be employed to measure bone mineral density accurately. This information influences the selection of implant type and size, potentially improving outcomes and reducing the risk of complications post-surgery. Understanding the density and structure of the bone also informs decisions regarding the treatment timeline and postoperative care.
How Imaging Informs Surgical Decisions
Diagnostic imaging plays a crucial role in surgical planning, providing a detailed view of the anatomical landscape. Techniques such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) allow for precise evaluation of bone density and critical anatomical structures. These insights enable surgeons to make informed decisions regarding implant placement, angulation, and the selection of the appropriate size and type of implants. By visualising the three-dimensional relationships within the jaw, it is possible to minimise the risks associated with surgery, such as nerve injury or inadequate bone support.
Surgeons leverage imaging data to create tailored surgical guides that enhance accuracy during the procedure. With the incorporation of digital technology, the imaging process allows for virtual simulations of surgical outcomes. This helps in identifying potential challenges and optimising treatment plans before actual surgery takes place. Ultimately, integrating advanced imaging techniques into implantology enhances surgical precision, leading to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
FAQS
What are the primary 3D imaging techniques used in implant planning?
The primary 3D imaging techniques used in implant planning include Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and traditional computed tomography (CT). These techniques help provide detailed images of the bone structure and surrounding anatomy.
How do 3D models enhance the accuracy of implant placement?
3D models enhance the accuracy of implant placement by allowing clinicians to visualise the anatomical structures in three dimensions, facilitating better planning and simulation of the surgical procedure. This leads to more precise implant positioning and improved outcomes.
Why is digital imaging important in implantology?
Digital imaging is important in implantology because it offers higher resolution images, faster processing times, and enhanced diagnostic capabilities. It also allows for easier storage and sharing of images, which can improve collaboration among dental professionals.
How is digital technology integrated into the implant planning process?
Digital technology is integrated into the implant planning process through the use of software for image analysis, 3D model creation, and treatment simulations. This technology enables the development of customised treatment plans that cater to the individual needs of patients.
How does imaging help evaluate anatomy and bone density for implant placement?
Imaging helps evaluate anatomy and bone density by providing clear visualisation of the patient's jaw structure, including any variations or deficiencies in bone density. This information is crucial for determining the appropriate type and size of implants, ensuring successful integration and stability.
Related Links
Evaluating Bone Density and Quality in Pre-implant AssessmentsHow to Prepare for the Pre-operative Assessment Appointment
Collaborating with Specialists for Optimal Pre-operative Planning
Managing Patient Expectations During Pre-operative Consultations
Checklist of Pre-operative Requirements for Dental Implants
Importance of Treatment Planning in Complex Implant Cases